Page 42 - Demo
P. 42
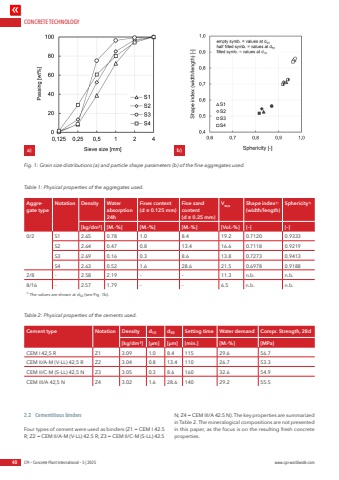
CONCRETE TECHNOLOGY40 CPI %u2013 Concrete Plant International %u2013 5 | 2025 www.cpi-worldwide.com2.2%u0009 Cementitious bindersFour types of cement were used as binders (Z1 = CEM I 42.5 R; Z2 = CEM II/A-M (V-LL) 42.5 R; Z3 = CEM II/C-M (S-LL) 42.5 N; Z4 = CEM III/A 42.5 N). The key properties are summarized in Table 2. The mineralogical compositions are not presented in this paper, as the focus is on the resulting fresh concrete properties.Fig. 1: Grain size distributions (a) and particle shape parameters (b) of the fine aggregates used.a) b)Table 1: Physical properties of the aggregates used. Aggregate typeNotation Density Water absorption 24hFines content (d %u2264 0.125 mm)Fine sand content (d %u2264 0.25 mm)Vw,s Shape index1)(width/length)Sphericity1)[kg/dm%u00b3] [M.-%] [M.-%] [M.-%] [Vol.-%] [%u2013] [%u2013]0/2 S1 2.65 0.78 1.0 8.4 19.2 0.7120 0.9333S2 2.64 0.47 0.8 13.4 16.6 0.7118 0.9219S3 2.69 0.16 0.3 8.6 13.8 0.7273 0.9413S4 2.63 0.52 1.6 28.6 21.5 0.6978 0.91882/8 %u2013 2.58 2.19 %u2013 %u2013 11.3 n.b. n.b.8/16 %u2013 2.57 1.79 %u2013 %u2013 6.5 n.b. n.b.1) The values are shown at d50 (see Fig. 1b). Table 2: Physical properties of the cements used.Cement type Notation Density d10 d50 Setting time Water demand Compr. Strength, 28d[kg/dm%u00b3] [%u00b5m] [%u00b5m] [min.] [M.-%] [MPa]CEM I 42,5 R Z1 3.09 1.0 8.4 115 29.6 56.7CEM II/A-M (V-LL) 42,5 R Z2 3.04 0.8 13.4 110 26.7 53.3CEM II/C-M (S-LL) 42,5 N Z3 3.05 0.3 8.6 160 32.6 54.9CEM III/A 42,5 N Z4 3.02 1.6 28.6 140 29.2 55.5